- Retour accueil
- Vous êtes ici : Blog The Pyramids of the Cold v2 The Pyramids of the Cold Section 3 • The Egyptian metaphorical deification of the water cycle
The Pyramids of the Cold Section 3 • The Egyptian metaphorical deification of the water cycle
Publié par Bruno Coursol dans The Pyramids of the Cold v2 le 13/05/2023 à 19:27

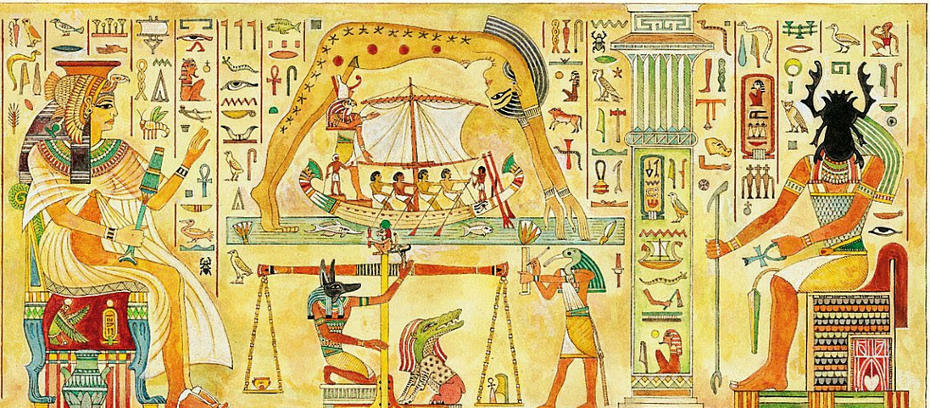
Scene from the astronomical ceiling of the Hypostyle Hall of the Dendera Temple of Hathor at Lunet (Lunet is the ancient Egyptian name of Dendera), showing 'goddess of the sky' Nut with her entire body made of water, as indicated by the very large blue water ripple signs on her body. Photographs thanks to Kairoinfo4U : https://www.flickr.com/photos/manna4u/9293995463/in/photostream/
The Pyramids of the Cold v2 (May 2023) • Part A: the evaporative cooling
Section 3 • The ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses of the Cold
In summary: deities like Shu, Geb, Nut and Tefnut are referring to the basic fundamental physical laws that are explaining the evaporative cooling process. Shu is the representation of dry and warm air, Geb is the representation of water in liquid form, Nut is the representation of the evaporated water (water in the sky), and Tefnut is the representation of liquid water in form of microdroplets (that is spat water, as 'tf' means 'to spit').
Additionally to these "fundamental" gods, other gods were also directly referring to the practical application of these scientific concepts : they were the "experimental" gods, like Apep (the pressurized waters of the inclined well), Atum (the small amount of that pressurized water ejected towards the evaporative passage), Nefertem (the water supply pipe of the fog nozzle and the fog nozzle itself) and Amun, the "invisible" King of Gods that was representing the evaporative process strictly speaking and thus, creating the cold.
Additionally to these "fundamental" gods, other gods were also directly referring to the practical application of these scientific concepts : they were the "experimental" gods, like Apep (the pressurized waters of the inclined well), Atum (the small amount of that pressurized water ejected towards the evaporative passage), Nefertem (the water supply pipe of the fog nozzle and the fog nozzle itself) and Amun, the "invisible" King of Gods that was representing the evaporative process strictly speaking and thus, creating the cold.
3.01 The link between the water of the Nile (Hapi) and the Dendera Light womb of Nut : Geb, the "god of the earth"
"Hapi (Ancient Egyptian: ḥʿpy) was the god of the annual flooding of the Nile in ancient Egyptian religion. […] Hapi was not regarded as the god of the Nile itself but of the inundation event. He was also considered a "friend of Geb", the Egyptian god of the earth." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hapi_(Nile_god)
In my opinion, Geb is actually a lot more than just a friend, because Geb, as Hapi and Nut, is all about water.
On this scene representing Nut, water is here clearly represented. In the same scene below, water is not represented, but it is though suggested by the solar boats, the fisherman, the fishing net and the postures of Geb and Nut. Goddess of the sky Nut is clearly diving into the water. Geb is not represented because he is the water. Shu is also not represented because he is the sail of the boat.
3.02 The solar boats sailing onto Nut, the fisherman and the fishing net clues indicating that Nut = Water
Many clues are actually clearly suggesting that Nut is all about water:
• The fact that solar boats are sailing directly onto her body.
• The fact that a fisherman is represented with half his body immersed into water : he simply appears cut in half.
• The fact that the fisherman is throwing a fishing net.

Papyrus mythologique de Tanytamon, Egyptien 172. Bibliothèque nationale de France, département des manuscrits (color and luminosity modified on gimp): https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/btv1b8304598h
3.03 Shu is not separating Geb from Nut, he is holding her in the air: Shu is forcing moisture to accumulate in the air
In my opinion, that scene of Geb and Nut separated from each other by Shu is actually representing the cycle of water between its liquid form and its evaporated form.
Nut is getting out of the water (her lower body) and then comes back in with her upper body.
3.04 So why Nut is described as the goddess of the sky and Geb as the god of the earth ?
We've just seen that Nut and Geb were both representing water, but in two different forms: liquid water (Geb) and evaporated water (Nut). Once you take the water out of the equation, the only elements remaining is the earth (where the liquid water is) and the sky (where humidity and moisture are).
This is why today, egyptologists say that Geb is the god of the earth and Nut the goddess of the sky.
They are just missing the water.

Scene showing Geb (back swimming into liquid water), Nut (represented diving into the water), and Shu in the center, "holding" goddess Nut: https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fichier:Geb_and_Nut03.png.
Diving drawing: https://www.mobilesport.ch/plongeon/plongeon-basics-chute/
Backstroke technique: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Backstroke_(PSF).png
3.05 Why is nobody pointing out the relation of Nut with water despite her water-pot emblem and the similarity of her name with Tefnut who is the goddess of moisture?
I think the reason is that nobody really wants to talk about the water. It is that simple. But if you do that, not only you can't understand the Dendera Light, but you can't understand "god of the earth" Geb either.
For egyptologists, water doesn't deserve to be studied for anything else but agriculture, even though the expression "the power of water" appears in many occasions in the Book of the Dead, as well as the one we've just seen : "the protective magical energy in liquid form" about the Dendera Light.
If you don't think about water in the famous Geb and Nut paintings where Shu is represented "separating" them both, you can't understand their respective postures.
If you do think about water you understand that:
1 • Geb is swimming: Geb is a representation of liquid water (on earth) = god of the water on earth
2 • Nut is diving into the water from the air: Nut is a representation of humidity / moisture = goddess of water in the sky
3 • Shu (god of dry warm air and fog) is the one receiving / holding / sustaining / supporting that humidity and he is the one separating them both
In short, the Geb and Nut scene is all about the evaporative process that is the motor of the evaporative cooling.

The ancient Egyptian goddess "of the sky" Nut, in the Temple of Hathor at Dendera. Thanks to Hamerani on Wikimedia Commons: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Temple_of_Hathor_at_Dendera._The_goddess_Nut.jpg
3.06 The link between the water of the Nile (Hapi) and the Dendera Light womb of Nut: Geb, the "god of the earth"
"Hapi (Ancient Egyptian: ḥʿpy) was the god of the annual flooding of the Nile in ancient Egyptian religion. […] Hapi was not regarded as the god of the Nile itself but of the inundation event. He was also considered a "friend of Geb", the Egyptian god of the earth." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hapi_(Nile_god)
In my opinion, Geb is actually a lot more than just a friend, because Geb, as Hapi and Nut, is all about water.
3.07 God Shu (spat out by the Serpent Atum) was associated with dry warm air, cooling and fog
"The ancient Egyptian god Shu is represented as a human with feathers on his head, as he is associated with dry and warm air."
"As the air, Shu was considered to be a cooling, and thus calming, influence, and pacifier. Due to the association with dry air, calm, and thus Ma'at (truth, justice, order, and balance), Shu was depicted as the dry air/atmosphere between the earth and sky, separating the two realms after the event of the First Occasion."
"Fog and clouds were also Shu's elements and they were often called his bones. Because of his position between the sky and earth, he was also known as the wind."
Source: Wikipedia page on ancient Egyptian god Shu: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shu_(Egyptian_god)
3.08 Goddess Tefnut (also spat out by the Serpent Atum) was associated with spat water and moisture
"Tefnut (tfnwt) is a deity of moisture, moist air, dew and rain in Ancient Egyptian religion."
"Literally translating as "That Water", the name Tefnut has been linked to the verb 'tfn' meaning 'to spit'."
Source: Wikipedia page on ancient Egyptian goddess Tefnut: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tefnut

Ancient Egyptian representation of a basic fundamental principle of physics and its application for the production of evaporative cooling in the Great Pyramid of Giza.
The ancient Egyptian gods (and the Great Serpent of the Underworld Apep) involved in the cold production of the Lower Great Pyramid of Khufu : Atum who created 2 other gods by spitting them out of his mouth : Shu (the god of dry warm air and fog), and Tefnut (the goddess of moisture and humidity) ; and Nefertem that represented the fog nozzle itself, and who "had arisen from the primal waters" and was the "beautiful one who closes" or "one who does not close"; as a perfect "tap" or "valve" analogy.
"In the Book of the Dead, [...], the sun god Atum is said to have ascended from chaos-waters with the appearance of a snake, the animal renewing itself every morning."
3.09 The Serpent god Atum spat out Shu, the god of air, and Tefnut, the goddess of moisture
"Early myths state that Atum created the god Shu and goddess Tefnut by spitting them out of his mouth. Other myths state Atum created by masturbation…"
"He produced from his own sneeze, or in some accounts, semen, Shu, the god of air, and Tefnut, the goddess of moisture."
My comments : when it is said Atum was created by masturbation, it is of course another metaphor here. When Isis is breastfeeding Horus, it is not milk he is receiving, but the cold liquid solution ; the same way when Atum is depicted masturbating, or when semen is invoked, it is only a way of depicting the high pressurized water coming out of the fog nozzle into microdroplets.
Once again, there is no breastfeeding, no masturbation, no semen and no spitting snake (see the Dendera Light post). These are only metaphors of the cooling fluids and the fog nozzle functioning with pressurized water.
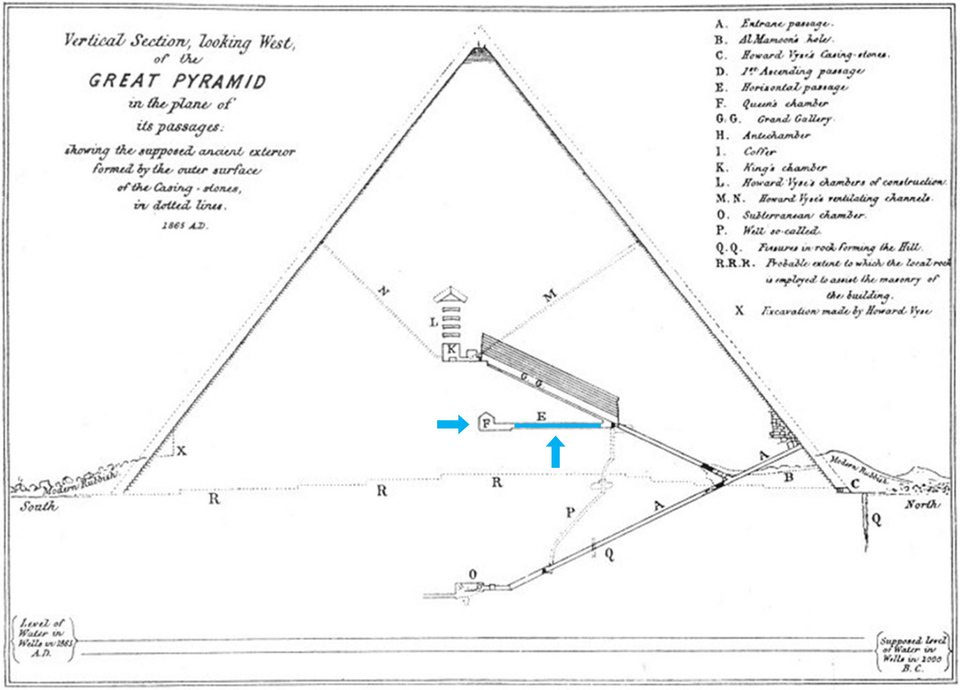
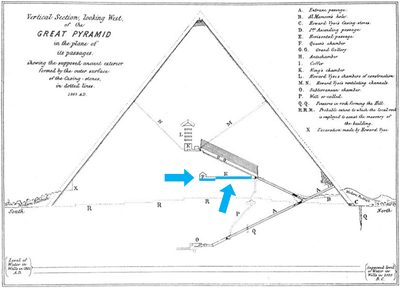
Vertical section, looking West, of the Great Pyramid of Giza, in the plane of its passages, by Manly Palmer Hall: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:The_Secret_Teaching_of_All_Ages_-_Chapter_6_-_Pyramid.jpg
3.10 The scientific metaphoric representations of the ancient Egyptian gods
Every single ancient Egyptian deity is only a metaphor, and they all are about a particular aspect of scientific research and technological experimentations they've started probably with the very first Dynasty. Even if some of these deities appeared before the Great Pyramid was built, most of them are directly referring to how was created evaporative cold in the horizontal passage of the Pyramid, and how was this process based on.
For example, the combined representations of Shu, Geb and Tefnut are a perfect illustration of the evaporative process that is transforming liquid water, into evaporated water; this process being supported by Shu, the god of dry and warm air.
3.11 The impactor ramming into the inclined well waters (Nun) to produce pressurized water (Apep)
I've already talked about the distinction that has to be made between the waters of the well before the pressurization and the pressurized waters strictly speaking.
The "plain still" waters had been glorified into what have been called the primordial waters of Nun, while the pressurized waters had been represented into the Great Serpent Apep (also Apophis).
This passage talks about how Atum created everything in human form out of the chaos: "At the beginning of time, when there was nothing but chaos, the sun-god existed alone in the watery mass of Nun which filled the universe. "I am Atum when he was alone in Nun, I am Ra when he dawned, when he began to rule that which he had made."
Once the well is pressurized, a small amount of that water is ejected into the horizontal cooling passage, and that is Atum: about 200 liters of pressurized water which every 15 minutes or so passes through the fog nozzle to create a fog of microdroplets of liquid water. This very particular form of water had been glorified into goddess Tefnut (Tef, or 'tf', meaning to spit).
"He (Ra) created Shu, god of air, and the goddess of moisture, Tefnut." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ra
The above excerpt is by the way, another confirmation that the purpose of the impactor was not limited to produce pressurized water: if Ra is the one creating Shu, the god of dry and warm air, it is because the fall of the impactor is taking place inside a fixed wooden caisson that was perfectly extending the inclined well, probably to the top of the Grand Gallery.
3.12 The Primeval Hill on which Ra is creating Shu and Tefnut is the Grand Gallery
"On a Primeval hill, Ra created out of himself the first gods, Shu (Dryness and Air), and his partner Tefnut (Humidity), who would engender other gods to complete the Cosmos: Geb the Earth god and Nut the Sky goddess." https://www.arce.org/resource/ra-creator-god-ancient-egypt
Everyone would have most probably recognized in the "Primeval Hill", the steep slope of the Grand Gallery, precisely where the impactor Ra was operated.

Diagram of the main ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses involved as simple metaphoric glorifications, in the operating of the Great Pyramid of Egypt for evaporative cold production (see next Sections for details).
3.13 Ra as Atum and the Creation process out of Water
Also from Arce : "Before creation, according to Egyptian mythology, only Darkness embraced the Primeval Ocean out of which life would come. When the breath of life was strong and ready, the entity called Atum decided it was time for Creation to begin. An island emerged from the water to support this divinity, who manifested itself in the form of Ra, the sun god of Egypt."
This particular phrase "When the breath of life was strong and ready, the entity called Atum decided it was time for Creation to begin" could be another confirmation that before the well was pressurized, the fall of the impactor first pushed air in front of him. The fixed wooden caisson in which was moving the impactor would have function exactly like a bicycle pump and would have pressurized the evaporative cooling passage with the air of the caisson, before the pressurization of the inclined well waters.
Atum, originating from the well and being the one metaphorical god just before creation could happen, is the "small amount of pressurized water", maybe about 200 liters, that were ejected from the well every 15 minutes or so, towards the fog nozzle.
"Ra was believed to have created all forms of life by calling them into existence by uttering their secret names. In some accounts humans were created from Ra's tears and sweat."
"According to one myth the first portion of Earth came into being when the sun god summoned it out of the watery mass of Nun."
"Ra was thought to travel on the Atet, two solar barques called the Mandjet (the Boat of Millions of Years) or morning-boat and the Mesektet or evening-boat. These boats took him on his journey through the sky and the Duat – twelve hours of night which is also the literal underworld of Egypt. While Ra was on the Mesektet, he was in his ram-headed form." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ra
3.14 Nefertem : the mediator in which Atum is passing through
Excerpt from Michael J. Masley: "Meeks points out that the relationship between the sun and the lotus-Nefertem is well attested in the Pyramid Texts but the birth of the sun-god in the lotus blossom is known only after the Amarna period. Pyramid Texts Spell 249 (Pyr. § 266a): xa (wnjs)| m nfr-tm m zSSn r Srt ra “Unis will appear as Nefertem, as the lotus at the sun-god’s nose” corresponds to the image of the Egyptian deities giving life (anx) to the nose of the king and thus the life-force of the creator god Atum is transmitted to the sun-god Re through Nefertem. As such, Nefertem is a mediator that connects the two great gods."
3.15 The Nefertem "close or not close" reference. From Wikipedia: "Nefertem, possibly "beautiful one who closes" or "one who does not close", (also spelled Nefertum or Nefer-temu) was, in Egyptian mythology, originally a lotus flower at the creation of the world, who had arisen from the primal waters". https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nefertem
"Close or not close" is not a bad definition for what was really representing Nefertem: the fog nozzle of the horizontal passage. This nozzle was eventually nothing else than a huge water tap that transformed pressurized water from the inclined well (the ascending passage) into a mist of microdroplets of liquid water. There was no valve though, just the fall of the impactor inside the grand gallery of the Great Pyramid that pressurized the well.

3.16 No one ever questioned the fact that Nut, the so-called "goddess of the sky" had a water-pot as emblem?
According to Wikipedia's page on Tefnut, 'tfn' means 'to spit : "Literally translating as "That Water", the name Tefnut has been linked to the verb 'tfn' meaning 'to spit' and versions of the creation myth say that Ra (or Atum) spat her out and her name was written as a mouth spitting in late texts". Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tefnut
But according to https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/tfn, 'tfn' means orphan: "Conventional anglicization: tefen. orphan".
The correct translation for 'to spit' would be 'tf' and not 'tfn': "Etymology 2: (intransitive) to spit (+ m: to spit (something) out) [Pyramid Texts, rarely later]". https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/tf
3.17 Tefnut = 'to spit' + Nut. It means that Nut is referring to water
If Wiktionary is right over Wikipedia, that means that Tefnut, 'tfnwt' is 'tf' + 'nwt' = to spit + 'nwt'
If Tefnut means "that water" and is referring to spat water, then Nut 'nwt' is referring to water itself. Hence the water-pot emblem of goddess Nut.
3.18 The theoretical evaporative process of the cold production
What is remarkable with the Geb and Nut scene, is that it is a representation of the evaporative process that is producing the cold inside the Great Pyramid.
We've already seen in the first post about the Dendera Light, that ancient Egyptians loved to show and explain what they were doing, in their own way of course : they've represented a snake spitting out its venom on one side of a relief, and just next to it, they've represented the Dendera Light with the same snake inside the bulb, and by doing so they were saying that the Dendera Light was created by the venom of the snake, as a metaphor of the spat water getting out of the fog nozzle, under pressure and in the form of microdroplets.
3.19 The sociological modern drama interpretation of Geb and Nut
"There is speculation between Shu and Geb and who was the first god-king of Egypt. The story of how Shu, Geb, and Nut were separated in order to create the cosmos is now being interpreted in more human terms; exposing the hostility and sexual jealousy. Between the father-son jealousy and Shu rebelling against the divine order, Geb challenges Shu's leadership. Geb takes Shu's wife, Tefnut, as his chief queen, separating Shu from his sister-wife. Just as Shu had previously done to him." https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nut_(goddess)

3.14 God of magic Heka's role was "to proclaim the pharaoh's enthronement"
The idea that pharaohs used scientific knowledge to legitimate their position as Kings of Egypt, is exactly what is said about the ancient Egyptian god of Magic, Heka (ḥk3w).
"The Old Kingdom Pyramid Texts depict ḥk3w as a supernatural energy that the gods possess. The "cannibal pharaoh" must devour other gods to gain this magical power. Eventually, Heka was elevated to a deity in his own right, and a cult devoted to him developed. By the time of the Coffin Texts, Heka is said to have been created at the beginning of time by the creator Atum. Later Heka is depicted as part of the tableau of the divine solar barge as a protector of Osiris capable of blinding crocodiles. Then, during the Ptolemaic dynasty, Heka's role was to proclaim the pharaoh's enthronement as a son of Isis, holding him in his arms."
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heka_(god)
Of course, you'll have noted that Heka is holding snakes : Heka's magic was coming from snakes, meaning that magic was coming from water. Snakes = water.
Remember, Atum is the representation of the small amount of pressurized water coming from the inclined well. Atum is liquid water ready to be transformed into vapor and this is this transformation that is creating the evaporative cold.
When it is said that "Heka existed before duality had yet come into being", the duality is about water. Duality is about liquid water and evaporated water that are engaged into the water cycle depicted into the famous Geb, Shu and Nut scene.

On the two stone reliefs on the right, Amun as Amun-Min, is clearly referring to water getting out of some kind of tube. These kind of reliefs are exceptional, because they also were clearly made by some kind of "street artist" who took the liberty to show something that is appearing in no other "official" relief I know of. These "unofficial" and probably "forbidden" reliefs are showing the true nature of Amun: he was referring to water droplets, because of the dotted line.
3.15 Amun is the personification of the fog of microdroplets evaporating and creating the cold
Amun, being the fog of liquid microdroplets that was created by the fog nozzle of the horizontal cooling passage, to evaporate and create the cold, is explaining of Amun's epithets: "Great Honker/Great Shrieker".
"Amun’s many epithets included: Great Honker/Great Shrieker (An allusion to his mythological role as the goose whose cry created the universe)." https://mythopedia.com/topics/amun
This reference to the sound that would have created the pressurized water passing through the fog nozzle, isn't the first one we've seen about the functioning of the nozzle, and that was personified into god Nefertem.
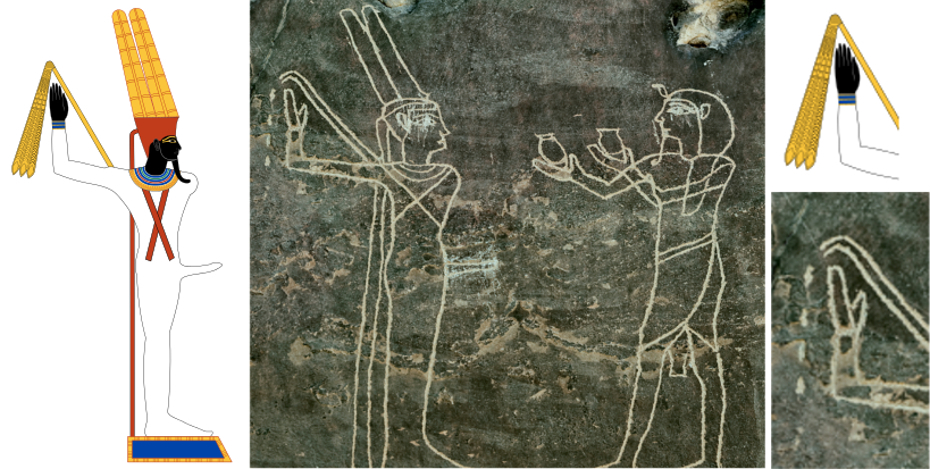

Amun as Amun-Min, drawing by Jeff Dahl: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Min_(god)
Stone relief at Wadi Hammamat, Dynasty 17 by kairoinfo4u: flickr.com/photos/manna4u/25999304796/in/photostream/

Wadi Hammamat: Dynasty 11, Nebhepetre Mentuhotep II. Photographed by Kairoinfo4U and posted on flickr: https://www.flickr.com/photos/manna4u/25932728632/in/photostream/

Heka figurine E4875 from the Louvre Museum: https://collections.louvre.fr/en/ark:/53355/cl010011666
Unmanned RB 6 fog nozzle monitor for firefighting and cooling from Rosenbauer International AG, Leonding, Austria.
"Heka is said to have been created at the beginning of time by the creator Atum."
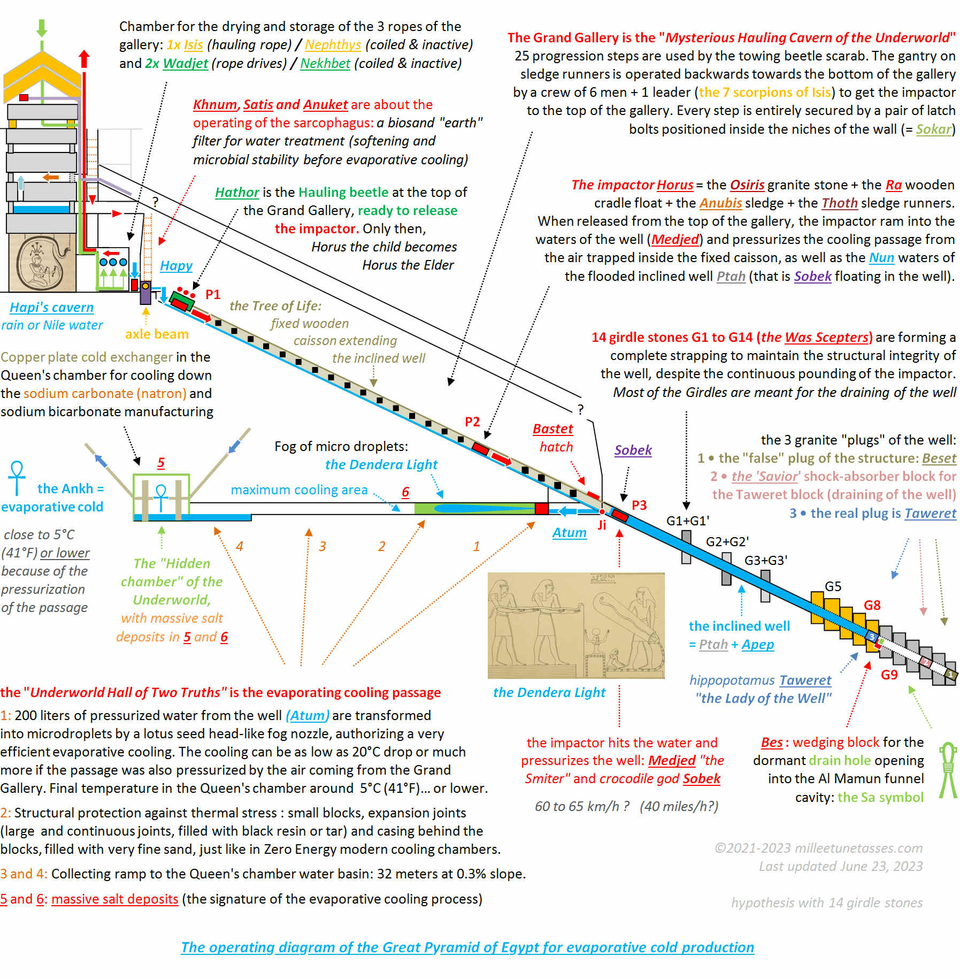
Diagram of the operating Great Pyramid of Egypt for evaporative cold production (hypothetically for chemical manufacturing cooling of pure sodium carbonate "natron", the salt used for the mummification of pharaohs). When in operation, the elevation of the Great Pyramid was not finished, and it is only after the shutdown procedure and the draining of the inclined well, that the 3 granite plugs were finally close to one another.

The Pyramids of the Cold version 2 (May 2023 - May 2024)
Summary of the study and Table of Contents
Part A: The evaporative cooling process
Section 1 • The horizontal evaporative cooling passage layout
Section 2 • The Dendera Light and the creation of the fog of microdroplets by the fog nozzle
Section 3 • The water cycle glorifying metaphors: Geb, Shu, Nut, Tefnut
Section 4 • The theorization of the evaporative cooling process by Akhenaten and Nefertiti
Section 5 • The theorization of the evaporative cooling process in the Weighing of the Heart
Part B • The inclined well of the Great Pyramid of Giza
Section 6 • The inclined well layout and the girdle stones
Section 7 • The Taweret "Lady of the Well" temporary sealing granite plug of the well
Section 8 • The Bes temporary wedging block immobilizing Taweret
Section 9 • The draining of the well
Section 10 • The Great Serpent Apep and the snake water metaphors
Section 11 • The Was scepter and the control over "snakes"
Section 12 • The beating Heart of the Great Pyramid
Part C • The composite impactor of the Great Pyramid (Horus, Ra, Osiris, Medjed, Sobek...)
Section 13 • The wooden and stone composite design of the impactor: Ra and Osiris
Section 14 • The endlessly immersed Osiris stone and the seed metaphor
Section 15 • The Anubis sledge and the bobsled mask
Section 16 • The sledge runners of the impactor: Thoth
Section 17 • Medjed: the smiter nobody can ever see
Section 18 • The Apis bull and the ramming impactor's metaphors
Section 19 • The crocodile god Sobek impactor (more or less) floating in the waters of the well
Section 20 • The Obelisk and the Benben stone rising from water
Part D • The Grand Gallery's of the Great Pyramid of Giza
Section 21 • The Sacred "sloping paths" of the "oval-shaped cavern of the act of Hauling"
Section 22 • The central wooden caisson of the Gallery: Sekhmet and the Triad of Memphis
Section 23 • The hauling ropes of the Grand Gallery: Isis, Nephthys, Hatmehit, Wadjet and Nekhbet
Section 24 • The hauling Beetle and the Seven Scorpions of Isis
Section 25 • The Great Cow goddess Hathor and the operating cycle of the hauling Beetle
Section 26 • The 10 operating phases of the Grand Gallery
Section 27 • The guide to the Afterlife for the smart traveler and the canopic jars
Section 28 • The scarab amulet glorifications of the hauling Beetle
Part E • The very large and roughly finished sarcophagus of the Great Pyramid
Section 29 • The biosand filter sarcophagus of the Great Pyramid
Section 30 • The Elephantine Triad deification of the biosand filter of the Great Pyramid
Section 31 • The Great Pyramid's operating flat roof and the water supply issue
Part F • Chemical manufacturing and industrial cooling before the Great Pyramid
Section 32 • The Serdab and the "Refreshment of the Gods" Step Pyramid of Djoser
Section 33 • Sneferu's Red Pyramid and the accumulated ammonia
Section 34 • The Disc of Sabu and the Solvay process for pure natron manufacturing
Part G • The tremendous impact of the Great Pyramid on the whole ancient world
Section 35 • The hidden secrets of the Hermetica Emerald Tablet (around 1600 C.E.)
Section 36 • Thor and the magical Hammer in the Great Hall of Bilskirnir
Section 37 • The Churning of the waters of the Ocean of Milk (Hindu mythology)
Section 38 • The Tibetan prayer wheels and the Grand Gallery's operation
Section 39 and Conclusion • The cooling water of spitting Kebechet
Part H • Epilogue
Section 40 • The smiting Ark of the Covenant and the Ten Commandments
Section 41 • The 293 kilograms windlass Staff of Moses and Aaron... and the First Plague of Egypt: water turning into blood
Section 42 • Ezekiel's Four Egyptian pulley "Wheels within the Wheels" and the four angel ropes
Section 43 • David, Saul, two giant Goliaths, five little stones, an aeolian harp... and a weaver's beam
Section 44 • The holy water fonts and the biosand filter
Part I • The magicians of the Great Pyramid of Giza
Section 45 • The Legend of Khufu and the "magician" polymath Imhotep
Section 46 • The two magical eyes of Isis and the brilliant but painful flame of her twin sister's braids
Section 47 • The Aegis Shield of Athena "Subduer of the Winds" and the upper hatch of the central wooden caisson
Section 48 • The Seven Magical Words spoken by 'Divine Sealer' Goddess of Arrows and Bronze Neith
Poster un commentaire